Assistant Professor
Dr. D.Y. Patil Biotechnology & Bioinformatics Institute
Working Period: January 2018 - May 2018
Dr. D.Y. Patil Biotechnology & Bioinformatics Institute
Working Period: January 2018 - May 2018
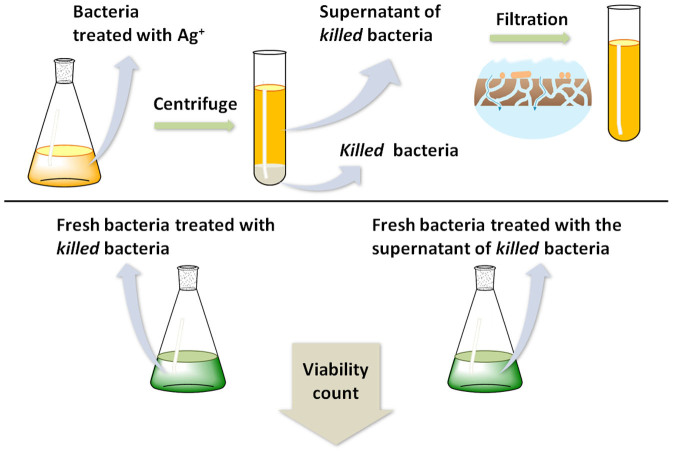
I joined Dr. Gaikwad's lab as a bachelor's student to complete my Bachelor's dissertation focusing on exploring the antimicrobial activity of bio-inspired silver nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
We chose Piper betel as the biological source for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles followed by performing several characterization techniques (UV-Visible spectroscopy, Scanning Electron Microscopy, Fourier Transform Infra Red Spectroscopy, and X-Ray Diffraction) to confirm the synthesis of silver nanoparticles (See below).
Our result suggested the right formation of the silver nanoparticles with the average size of the particle falling in the range of 20-40 nanometre. MIC calculation was undertaken to explore the inhibitory concentration of the nanoparticles against the bacterial culture. With an average MIC value of 120 ug/ml, we were able to successfully show the antibacterial property of our synthesised nanoaprticles.
The major application that our work proposes is in the field of wound healing. Applying the prescribed silver nanoparticles will allow for the destruction of the bacterial cultures. The dead bacterial culture acts as a reservoir for the subsequent attack thus acting as a "Zombie".
Since our experimental examinations showed a promising result, we wanted to explore the atomistic details of the interaction between the nanoparticles and the virulence proteins of the bacterial colony. We performed in-silico analyses such as Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulations to explore the molecular interaction between the synthesized silver nanoparticles and the virulence proteins, ExoS and ExoY, of Pseudomonas aeruginosa acting via the Type 3 Secretion System (T3SS).
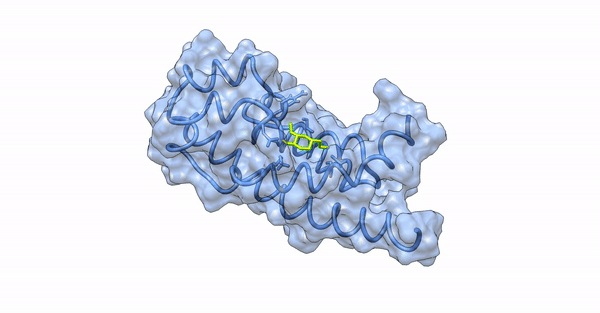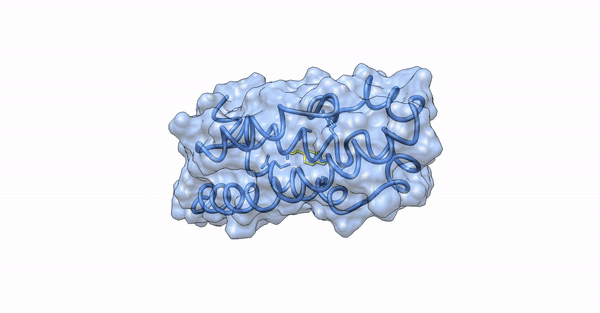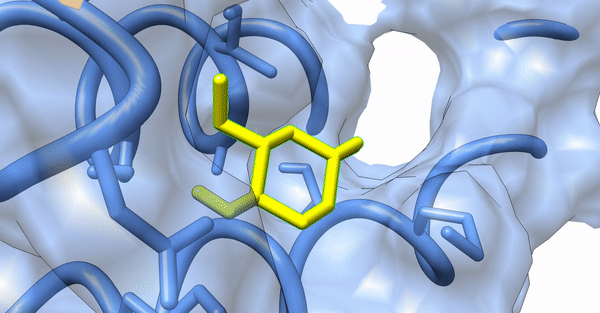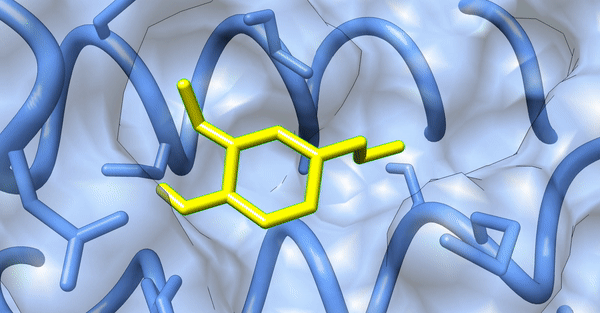
Phytochemical conjugated silver nanoparticles interacting with ExoS
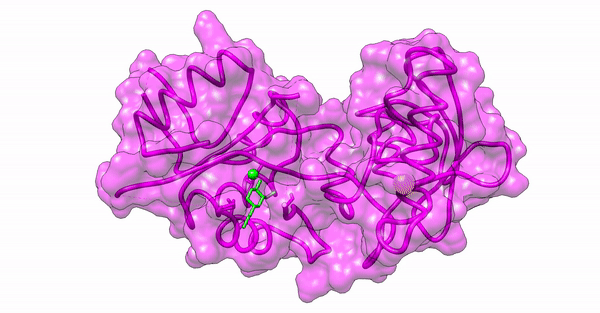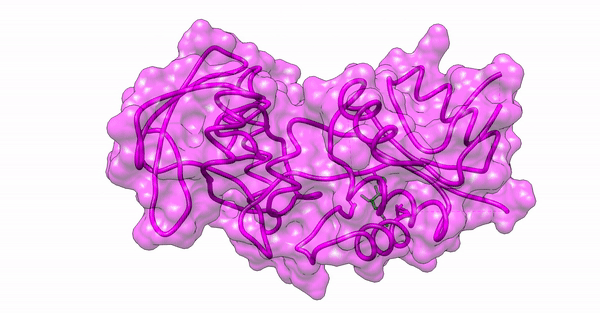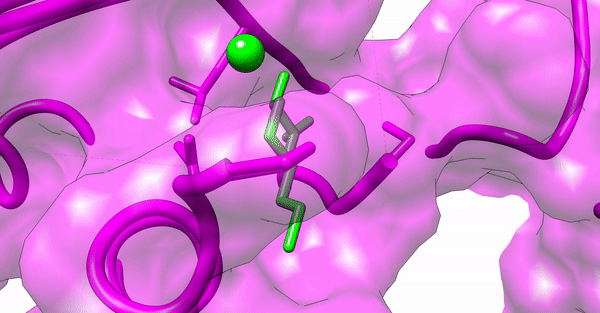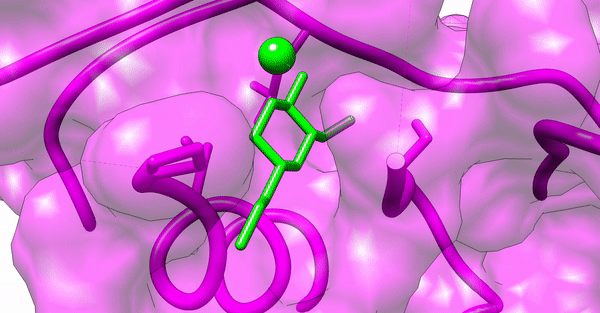
Phytochemical conjugated silver nanoparticles interacting with ExoY
Computational examination revealed microscopic details of the interaction between the ligand and the virulence proteins. We found that the synthesized nanoparticles had a better interaction profile than the commercial drugs available to treat bacterial diseases. Our synthesized nanoparticles not only showed a better pharmaco-kinetic behavior but were also efficient in showing better pharmacological parameters by following Lipinski's Rule of Five (RO5) and Toxicity studies.
To know more about our work, please look at our paper:
"Computational Approach to Attenuate the Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa through Bio-inspired silver nanoparticles"
Satyam Sangeet, Sarika Pawar, Neelu Nawani, Manisha Junarkar, Swapnil Gaikwad
3 Biotech (2022)